
By research and analysis of patent information of International PET detector through the patent information retrieval and analysis platform of CNIPA, this article makes an in-depth study of technical development of PET detector, analyzes the current global technological competition layout, and clarifies China's technical position in this field. It aims to provide a reference for the development of Chinese enterprises in this field. To facilitate analysis, this paper combines the usual detector technology research and development method, and analyzes the detector's technical branches, including five key technical branches of scintillator crystals, photovoltaic conversion, read-out circuits, overall planning, and multimodality utilization.
In recent years, PET imaging systems have begun to emerge in China's medical market.3 In China's "13th Five-Year" strategic plan, medical imaging equipment, including PET, has become the focus of the government's efforts to promote innovation and development. The Large Medical Equipment License Management Directory released by the National Health Commission of China in 2018, further relaxed the licensing rights for PET.4 In addition, the "First Set" policy was put forward by the Commission to help domestic equipment open up market and improve the process of domestic product substitution, encouraging priority in products that have achieved major technical breakthroughs in core components and IPRs in procurement. For domestic enterprises, it is a significant benefit. It can be imagined that if domestic enterprises can grasp the right direction and successfully realize the innovation of detector technology, it will soon be possible that domestic substitution for PET can be reached in the market.
By research and analysis of patent information of International PET detector through the patent information retrieval and analysis platform of CNIPA, this article makes an in-depth study of technical development of PET detector, analyzes the current global technological competition layout, and clarifies China's technical position in this field. It aims to provide a reference for the development of Chinese enterprises in this field. To facilitate analysis, this paper combines the usual detector technology research and development method,56 and analyzes the detector's technical branches, including five key technical branches of scintillator crystals, photovoltaic conversion, read-out circuits, overall planning, and multimodality utilization.
Analysis of application annual trend

Figure 1 Trend chart for the year of detector application
Figure 1 shows the trend of the year of the detector application, from which the detector application experienced a process from slow development to rapid take-off. Especially with the emergence of Time of Flight (TOF) in this century, the signal-to-noise ratio of the system has been greatly improved, the number of applications has also increased rapidly. The total number of applications since 2000 is three times more that the total in the previous 30 years. It can be said that, at present, the application of PET imaging system shows a trend of rise.
Regional comparison of patented technology
The country of the technology's origin can reveal the distribution of the patented technology in each country, while the distribution authorized in the IP5 bureaus (US, Japan, Europe, China, Korea) can also reveal the patented technology's strength in a certain area, and therefore understand the layout of the region.56
Table 1 Patent authorization of top technology source countries (pieces)

From "Total Applications" column in Table 1, the US (1014) and Japan (683) have the largest number in source countries, accounting for 71% of the total number of applications, as can be seen in the absolute leading position in the development of detector technology and the strong demand for the detector market. The total number of applications from China is 260, far behind the US and Japan, and the earliest applications from Chinese applicants were filed in 1997, almost 20 years behind the US. In 1997-2010, the number of applications from China cannot account for the tenth of the US and Japan. It was not until 2010 that applications from China for PET detector technology began to show a rapid growth trend.
Thanks to global technology penetration and the national "12th Five-Year" strategy, which support for "breakthroughs of 20-30 key technologies and core components, forming 200 core patents", the number of applications from China has been catching up since 2008 and has seen a small peak since 2012, surpassing Japan.
From the percentage of application authorization reflected in Table 1, applicants from the US demonstrate their strong technical leadership. US patent applications are not only high in numbers, but also high in licensing rate with 69% authorization rate. South Korea has a relatively small number of applications, but the licensing rate is also high at 63%. Japan has a licensing rate of 58%, and the percent of Germany and the European Trademark Office are 56% and 50% respectively. The number of first-time applicants in China, ranks the third, yet the licensing rate is only 29%. Based on the actual data, the vast majority of China's authorized invention patents are contributed by foreign applicants. It can be seen that China's technology development in the field of detectors is still lagging behind with developed countries.
In addition, from the licensing layout, the authorization rate of applications from the US is much larger in the US than in other countries. It can be seen that the US patent applicants pay less attention to other countries and regions than the US mainland. However, it is worth noting that, despite China's late start, in the past two years, China has overtaken Japan to become the the most important layout country for applicants from US, Japan, Germany other than the US. China is prosperous in this field, and has a lot to discover in technology protection, thus becomes a competitive layout country.
In addition to the high number of first-time applications from Japan (308 total), the number of authorizations in the US (145) is also considerable, indicating that applications from Japan prefers to apply in the US. The authorized patents from European applicants accounted for 41% of their global filings in the US, nearly twice the proportion of European mainland, which means that most European applications are layout in the US.
The number (21) of first-time applications from China which is also authorized in China is much higher than its authorized applications in the US (4), which indicates that the first application from China mainly layouts in China, on the other hand, it also shows that China's detector technology development is relatively lagging behind.
Analysis of detector patent technology research
1. Evolution of the hot spots of overall technology research
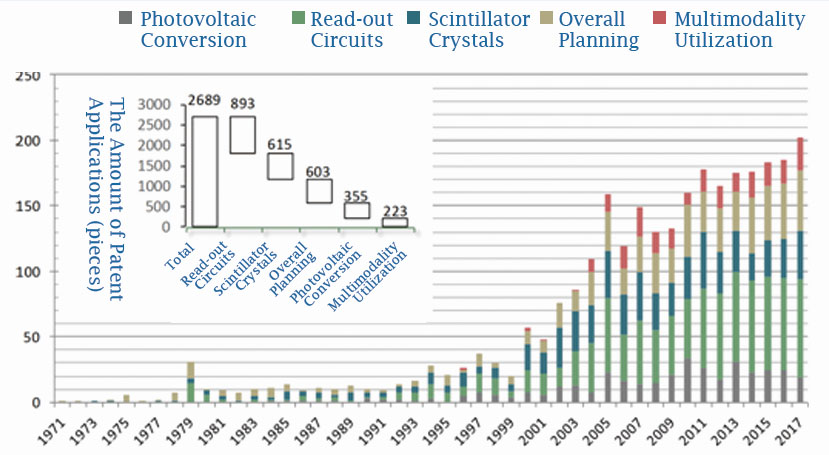
Figure 2 Global applications for the secondary technology branches of the detector and the cumulative application trends every three years
As can be seen from Figure 2, out of the global application for secondary technology branches of the detector, read-out circuits has the largest number of applications, reaching 893 pieces, followed by scintillator crystals (615 pieces), overall planning (603), photovoltaic conversion (355) and multimodality utilization (223). Since the most critical factor in compliance with detection is to accurately identify the position, energy and time information of photons, the read-out circuits technology has always been the focus of research and development in major enterprises and research institutions. Moreover, many enterprises have made considerable efforts, as scintillator crystals determine the degree of energy that destroys photons.
The column of "the cumulative application trends every three years" in Figure 2 provides a better picture of the popularity and evolution of various technical branches of the detector. It can be seen that the application scale of photovoltaic conversion technology since 2010 has been reduced year by year, showing a rapid decline. Read-out circuits has attracted high attention in the industry, which may be in relation with the fact that the structural or arrangement problems of silicon photomultipliers (SiPM) and avalanche photodiode (APD) have been overcome, and the focus has been shifted to solve the read-oud circuits' output signal sensitivity.
What is worth noticing is the relative change in the amount of scintillator crystals and overall planning application. Prior to 2006, the total number of applications for the overall planning of the detector had been lower than the total number of detector planning applications. Since 2010, the total number of applications for the overall planning of the detector has been comparable to that of the scintillator crystals, perhaps due to the crystal arrays have been cut more finely, and the technical problems of optical crosstalk and effective light absorption have been referred to the improvement of the overall planning of the detector. The multimodality utilization technology has only emerged from 2000, although the branch is currently under-applying, it is on a clear upward trend. With the clinical complement of PET-CT and PET-MRI for tumor information, the application volume of multimodality utilization has began to grow rapidly, and after 2005, it has become another research and development focus for enterprises.9
Application preferences of technical branches of each key country Comparison among the application preferences of the technical branches of each country, can give a glimpse of the concentration of technology in various countries in quantity, thus provide a reference for competition and cooperation among enterprises and governments.
2. Application preferences of technical branches of each key country
Comparison among the application preferences of the technical branches of each country, can give a glimpse of the concentration of technology in various countries in quantity, thus provide a reference for competition and cooperation among enterprises and governments.
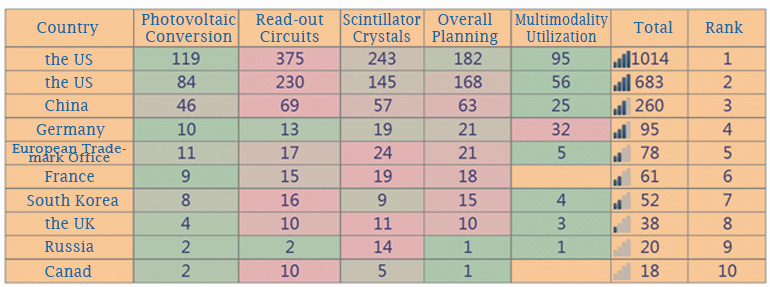
Figure 3 Application preferences of technical branches of each key country
(The redder the color, the more preferable the technology)
Figure 3 shows the application preferences of the technical branches of each key country, and it can be seen that each country has their own emphasis on different branches of detector technology. Among them, the US, Japan, and China's main applications are concentrated on read-out circuits, due to them being major electronics countries, but their application preferences are still different: the applications of read-out circuits are three times more than those of photovoltaic conversion in the US and Japan. This shows that the US and Japan can accurately grasp the trend of technology, and focus on the main research and development investment to read-out circuits, rather than the photovoltaic conversion that has already been in the technology saturation phase. Although China has an advantage in the number of applications of read-out circuits, it is not much different from other technology branches, which may be related to the shorter time china has taken in the overall development of detector technology, so the patent applications of various technology branches show a more balanced posture.
Germany mainly has applied in the multimodality utilization branch, because Siemens and other important German companies are committed to the development of PET-CT, PET-MRI magnetic field gradient, RF signal interference and other technologies, therefore, Germany's research and development efforts in the multimodality utilization are greater. France, South Korea, and the UK not only focus on read-out circuits, but also has bet considerable energy in the overall planning of technological innovation. Russia, for its part, is focused on technical improvements to scintillator crystals.
Conclusion
To sum up, PET detector technology is currently in the period of rapid development. From the technological point of view, photovoltaic conversion technology is currently underwater, and correspondingly, the multimodality utilization branch will be in a relatively fast upward momentum in the next few years, with the continued integration of PET to CT and MRI technology, although its start time is late. Chinese enterprises should consider investing more research and development effort in the branch to occupy the field ahead of time.
From the layout of the technology source region, the US and Japan occupy the absolute technological advantages, in the read-out circuits, forming its own patent group. At the same time, although the Chinese applicants in the read-out circuits started late, the volume of application growth is relatively fast while the authorization rate accounted for is relatively low. It can be seen that China's technical level in this field compared with other important countries still has a large gap.
Due to the late start of technology, China's applications in various technology branches are more balanced, taking into account that the US and Japan no longer prefer photovoltaic conversion, Chinese enterprises can develop their own detectors, considering at the same time the purchase of the US and Japan's core patents in the photovoltaic conversion branch, and even effectively using their invalid patents. It should also be noted that the current Chinese applicants' willingness to layout abroad is weak. The US has launched a "337 investigation" against China, and Chinese applicants may consider start patent defense in the potential market ahead of time. In addition, although the number of applications from South Korea is low, its authorization rate is ranked the third. Therefore, Chinese enterprises and governments should consider technical cooperation with South Korea to achieve a "win-win" situation. For the emerging multimodality utilization branch, Germany has significant technological advantages, Chinese enterprises and governments should also consider deepening technology integration with Germany in order to obtain more reasonable development.
|
Copyright © 2003-2018 China Intellectual Property Magazine,All rights Reserved . www.chinaipmagazine.com 京ICP备09051062号 |
|
|



